
2023 "SCIP+" Green Chemical and Chemical Innovation and Entrepreneurship Competition Suez designated proposition released
Since its launch in 2019, the "SCIP+" Green Chemical and Chemical Innovation and Entrepreneurship Competition has become one of the most influential innovation and entrepreneurship events in the industry. Entering its fifth year, the "SCIP+" competition will have the theme of "Green and Future", strengthen innovation and leadership around the needs of the chemical industry in the three major areas of "future materials, future energy, and future carbon cycle" to promote green development of the industry. The competition specially features enterprise-designated proposition units. Participants can provide project solutions or entrepreneurial practice results based on the innovation needs of enterprises. The designated proposition winning team will have the opportunity to in-depth docking with the proposition company to achieve win-win cooperation. The competition organizing committee will also successively release interpretations of propositions from competition partners to help participants better understand the needs of the company and optimize and polish innovative projects.
2023 SCIP Suez Enterprise Designation Proposition
Continuous-flow biological hydrogen production technology based on biomass recycling
Background description:Hydrogen energy is one of the important clean energy carriers and is receiving more and more attention. Hydrogen production technology based on biomass recycling focuses on the use of sustainable raw materials and is an important alternative to hydrogen production by electrolysis of water and traditional petrochemical raw materials. Among them, biological hydrogen production technology relies on the catalytic activity of enzymes to convert water molecules and organic substrates in biomass into hydrogen at room temperature and pressure. It is suitable for low-solid feed materials such as high-concentration organic wastewater, excess sludge, kitchen waste, Glycosylated cellulose and other raw materials.
However, in the industrialization process, related technologies still widely face problems such as difficulty in selecting microbial species, complex gas production components (difficulty in separation), low conversion efficiency, and poor continuity.
Company concerns:A team that can provide continuous flow biological hydrogen production technology and has good industrial application potential. The biomass raw materials involved in the technology are not clearly limited. In terms of technology selection, priority is given to dark fermentation technology, while the synergy between biological hydrogen production and other technologies is encouraged (such as hydrogen production/methane production synergy, microbial electrolytic cell MEC, etc.) to increase hydrogen yield.
Chemical energy storage technology for sustainable energy electricity
Background description:The production of clean energy electricity (such as wind power and solar power) usually has geographical limitations, which in turn brings difficulties in transmission, distribution and use. New energy chemical energy storage technology (internationally known as E-fuel) is a type of technology that uses clean energy generation to convert electrical energy into energy carriers that are easy to store and transport (such as gaseous fuels such as hydrogen or liquid fuels such as methanol). Solve the pain points of power storage.#### Company concerns:Mature technologies that can use green electricity to capture carbon dioxide and electrolyze water, as well as subsequent further synthesis of liquid fuels (such as methanol). There is no clear limit on the source of carbon dioxide captured, and technologies that can capture carbon dioxide tail gas from waste incineration are encouraged.
Physical and chemical recycling technology for waste plastics
Background description:China is a major country in plastics production and consumption. For a long time, a large amount of plastics that are not easy to recycle have entered waste incineration plants and been burned, converted into carbon dioxide emissions. In recent years, the promotion of classification and recycling of urban domestic waste is greatly promoting the process of plastic resource utilization. As Europe began to put forward clear requirements for the proportion of renewable plastics in imported plastic products, more and more production companies began to generate demand for recycled plastics. With the opening up of policies, the recycling of high-quality plastics such as "bottle to bottle" and their direct use in the production of food-grade plastic packaging has created huge market potential.
The main difference between "solid waste" and "resources" is that the former is a mixture of complex components, so it is necessary to strengthen the separation of target substances when carrying out resource recycling. How to balance the relationship between "separation of energy-consuming inputs" and "value output of recycled materials" has become an important concern when evaluating a technology.#### Company concerns:High-quality recycling technology for food-grade PET plastics, and a company or team that can quickly achieve large-scale industrial production. There will be no restrictions on the type of recycling technology (physical/chemical recycling), but the costs for separation and granulation will be carefully accounted for.
Biochar preparation and downstream application development
Background description:Biochar is a solid product obtained by thermal cracking of biomass under anoxic conditions. Its application in agriculture, environment, and low-carbon cycles has attracted widespread attention. Under different raw materials and preparation process conditions, the properties of biochar (such as specific surface area, functional group composition, water holding capacity, etc.) vary greatly, which in turn affects its downstream application scenarios. At the same time, the connection between downstream utilization of biochar and carbon credit certification has also aroused great interest in the industry.
Company concerns:A biochar preparation process suitable for large-scale production. We encourage preparation processes to focus on obtaining products with higher adsorption properties. At the same time, focus on companies or teams that can obtain voluntary carbon emission reduction certification through biochar preparation and utilization.
High-temperature thermal cracking and gasification technology for producing syngas
Background description:The resource utilization of low-quality biomass or carbon-containing solid waste (such as domestic waste such as low-quality plastics) is an important path to "turn waste into energy" and realize the replacement of petrochemical raw materials. Among them,"syngas" obtained through high-temperature thermal cracking and gasification technology is used as chemical raw materials, which may become an important alternative to waste incineration for power generation in the future. However, synthesis gas produced from low-quality materials usually has complex components and requires more complicated separation processes to enter the downstream utilization stage, so technological innovation is urgently needed.
Company concerns:Thermal cracking and gasification processes to produce synthesis gas using domestic waste and low-quality biomass as raw materials, and subsequent gas purification processes. We encourage teams in this field to consider maximizing the use of existing waste incineration facilities for renovation, supplemented by gas purification equipment, to produce high-quality syngas.
2023 SCIP Enterprise Introduction--SUEZFaced with increasingly severe environmental challenges, Suez Group has been committed to providing basic services to protect and improve people's livelihood for more than 160 years, and with its innovative and resilient solutions, it provides customers with water and solid waste services. The group's 40,000 employees in 40 countries actively empower customers, create value and promote low-carbon transformation throughout the entire life cycle of assets and services. In 2022, Suez Group will produce drinking water for 68 million people around the world and provide sanitation services to more than 37 million people. It will produce 3.7 TWh of energy through sewage and solid waste treatment and avoid 4 million tons of carbon dioxide emissions. Suez Group's revenue in 2022 will be 8.8 billion euros*。
immediately signed up *以12个月为基础进行核算。
参赛对象及要求
大赛设定创业创新组和创业实践组:
创业创新组参赛对象 高等院校和科研院所在读本科生和在读研究生、全日制非成人教育的本科生毕业生和研究生毕业生、高校青年教师以及企业青年科技工作者。
参赛申报人 须为项目负责人
参赛对象以“绿色·化未来”为主题,拥有创新科研成果,形成创新的产品升级建议或市场开拓建议,具有完善的项目建议书,可进行成果转化。
创业实践组参赛对象 已注册公司国内外初创企业和团队,应拥有基础产品、技术或服务原型,具备自有知识产权,寻求商业规模化。
参赛申报人须为公司和团队创始人、法定代表人或技术负责人。
赛程安排
启动和报名|6月27日—9月30日
各参赛团队通过大赛网站(http://plus.scip.com.cn)进行报名并提交参赛作品。
初选和复赛|10月—11月
10月,评审委员会按照评审规则,选出进入复赛的团队,组委会通过电子邮件、电话等方式通知复赛团队。
11月,组委会组织举行线上复赛,评选出进入决赛团队,组委会通过电子邮件、电话等方式通知决赛入围团队。
入围团队优化作品|决赛前
组委会将聘请行业专家对决赛入围团队进行赛前辅导,以获取更好的展示效果和更强的竞争力。
决赛|12月
参加决赛的团队进行现场展示,由产业、资本等行业专家组成的评审团队进行评审。
加速孵化|决赛后
对获奖团队进行为期一周的浸润式孵化培训,从创新思维、客户验证、产品/服务设计方面提供支持,建立可持续可规模化商业模式,进行影响力测试、项目路演及投资人对接会等。
大赛奖励
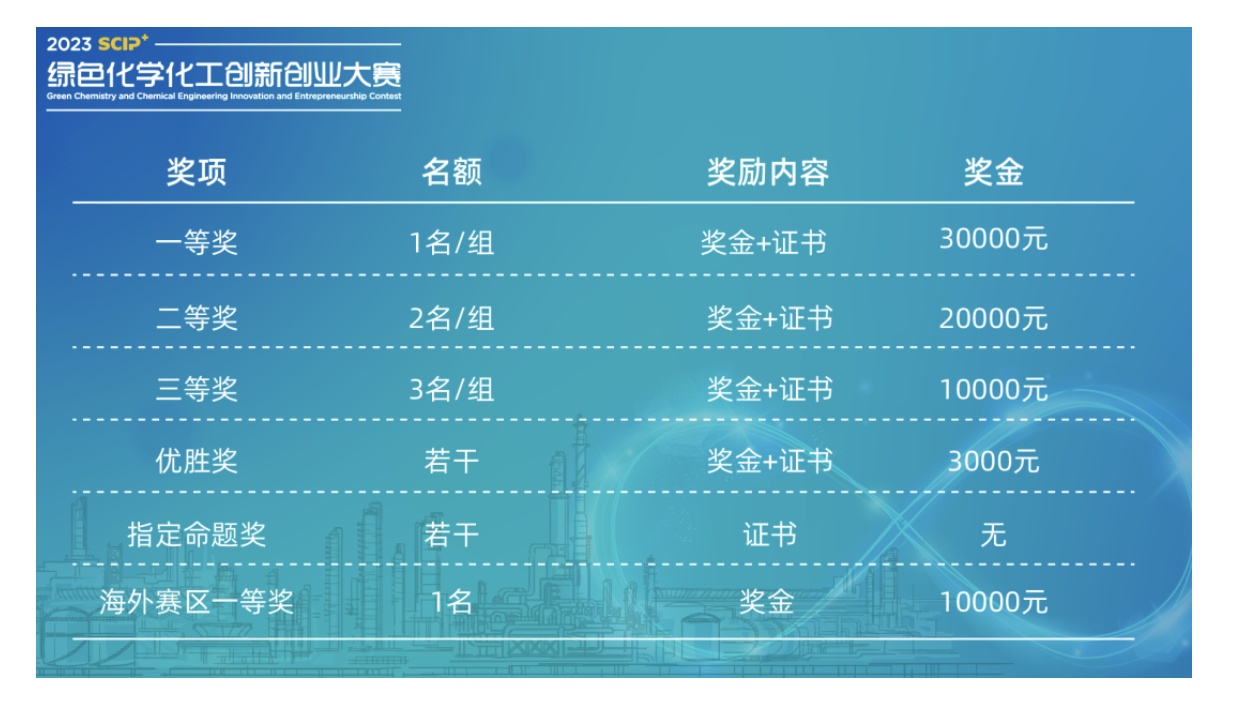
除奖金外,获奖项目还将有机会:
1、获得天使基金“雏鹰计划”资助。
2、进行浸润式商务考察和加速孵化以及与投资人对接。
3、与行业专家交流,开展产业对接应用落地和市场开拓。
4、获得上海化学工业区内上海国际化工新材料创新中心免费工位,以及享受相应扶持政策进行研发、小试、中试等活动(参照《上海化学工业区促进产业高质量发展专项扶持实施办法》)。
参与方式
各参赛团队可从电脑端进入大赛网站 http://plus.scip.com.cn 进行报名并提交参赛作品
如需咨询
欢迎添加 IH Fellow 微信(备注:SCIP)
